DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting & Conformance) is an email standard designed to help prevent email spoofing/phishing when used in conjunction with SPF and/or DKIM Certificate Generation. Additionally, DMARC gives the administrator the option to set the handling for the receiving server to handle the messages which fail the DMARC check. DMARC also provides the tools for domain administrators to receive reports of abuse of their domains.
We highly recommend configuring DMARC DNS records on all domains especially if your domain's are the target of spoofed emails. If you are unclear on how to setup DNS records please consult your DNS provider.
- Does Mail Assure Support DMARC?
- What are the specifications for DMARC?
- How to Set up a DMARC Record?
- Configuring DMARC Checks in Mail Assure
- Skip Specific Domains from DMARC Checks
- Skip Specific IPs from DMARC Checks
Yes, Mail Assure fully supports DMARC on all incoming mail. Outgoing messages may be DMARC checked by the recipients server if a DMARC record is published on the sending domain.
No DMARC checks are enforced on outgoing email by the outgoing filter.
DMARC allows the domain owner/administrator to carry out additional verification on messages claiming to be from their domain. It uses SPF on both the envelope sender address and the header FROM address, plus checking the alignment of these two addresses (i.e. do the domains match for both addresses). It also checks that the DKIM signing domain matches the sender address domain.
If any of the components of DMARC fail, the message will be handled as the policy in the DMARC record states i.e. Quarantined, Reject, None.
DMARC allows domain administrators to receive a RUF (forensic) report and RUA (aggregate) report for any message which has failed DMARC with their domain as the sender address.
More information on how DMARC works can be found here:
- https://dmarc.org/wiki/FAQ
- RFC 7489 - Full technical specifications of the DMARC internet standards
DMARC records are set up in the domain's DNS (Domain Name Server). When you set up your DMARC record you choose the policy type (reject, quarantine, none). This record tells the server what should happen to messages that fail SPF/DKIM checks.
An example of the most basic usable record for spoofing prevention is:
Host: _dmarc.yourdomain.invalid Record (TXT): v-dmarc1; p=quarantine; rua=mailto:postmaster@yourdomain.invalid
The following online resource may help:
Online tools are available to help build the DMARC record which can then be added to your DNS.
Skip Specific Domains from DMARC Checks
At times you may need to skip this check for a specific sending domain on the inbound filter so that any messages claiming to be from that domain (both SMTP sender address and the header FROM address) will bypass the DMARC check.
- In the Domain Level Control Panel, select Incoming - Protection Settings > Filter Settings
- Click the Manage list of domains and IP addresses with disabled SPF, DKIM, and DMARC checks link at the top of the page
- Navigate to the Disabled DMARC Domains tab
- In the Add a Domain panel, enter the domain name in the Domain field and click Add
Any messages claiming to be from that domain (both SMTP sender address and header from address) will now bypass the DMARC check.
Entering your own domains in this field will dramatically increase the risk of receiving a malicious message with spoofed from addresses.
Skip Specific IPs from DMARC Checks
At times you may need to skip this check for a specific sending IP on the inbound filter so that any messages claiming to be from that IP (both SMTP sender address and the header FROM address) will bypass the DMARC check.
-
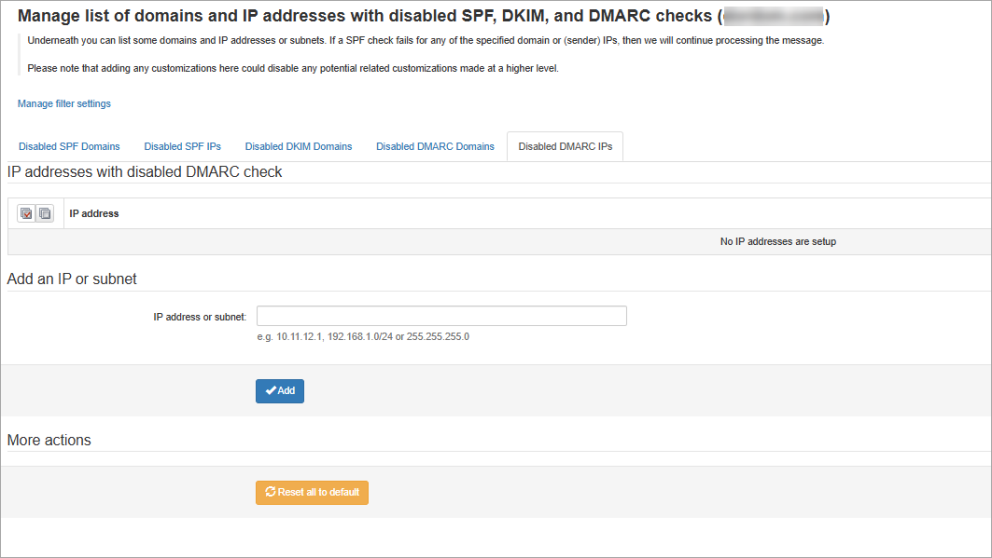
In the Domain Level Control Panel, select Incoming - Protection Settings > Filter Settings
-
Click the Manage list of domains and IP addresses with disabled SPF, DKIM, and DMARC checks link at the top of the page
-
Navigate to the Disabled DMARC IPs tab
-
In the Add an IP or subnet panel, enter the IP address or subnet in the IP address or subnet field and click Add
Any messages claiming to be from that IP (both SMTP sender address and header from address) will now bypass the DMARC check.
Entering your own IPs in this field will dramatically increase the risk of receiving a malicious message with spoofed from addresses.
Configuring DMARC Checks in Mail Assure
DMARC checks are enabled by default, we do not recommend disabling these.
To alter the DMARC checks within the Mail Assure filter: